Ski Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

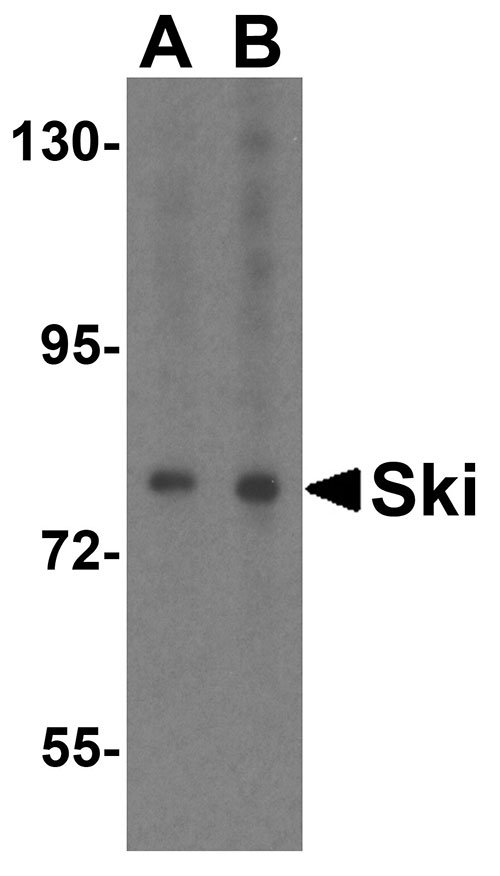
Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P12755 |
| Other Accession | P12755, 134517 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 80005 Da |
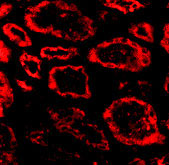
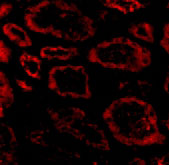
| Application Notes | SkiP antibody can be used for detection of Ski by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 20 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 6497 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Ski Antibody: SGS, SKV, Ski oncogene, Proto-oncogene c-Ski, v-ski sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (avian) |
| Target/Specificity | SKI; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Ski antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | Ski Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SKI |
|---|---|
| Function | May play a role in terminal differentiation of skeletal muscle cells but not in the determination of cells to the myogenic lineage. Functions as a repressor of TGF-beta signaling. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Ski Antibody: TGF-beta is a ubiquitously expressed cytokine that signals through the Smad protein family to regulate numerous cellular processes such as embryonic development and tumorigenesis. This signaling is negatively regulated by Ski, the mammalian homolog of the transforming protein of an avian retrovirus that induces oncogenic transformation of chicken embryo cells, and the related protein SnoN. Ski functions by binding to the Smad proteins and preventing their phosphorylation, thereby inhibiting their ability to bind DNA and activate the transcription of downstream genes. Ski will also bind to the Smad proteins specific to bone morphogenic proteins (BMPs) and block BMP signaling in mammalian cells.
References
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, and Balmain A. TGF-β signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat. Genet. 2001; 29:117-129.
Li Y, Turck CM, Teumer JK, et al. Unique sequence, ski, in Sloan-Kettering avian retrovirus with properties of a new cell-derived oncogene. J. Virol. 1986; 57:1065-72.
Luo K. Ski and SnoN: negative regulators of TGF-β signaling. Curr. Op. Gen. Dev. 2004; 14:65-70.
Massague J and Wotton D. Transcriptional control by the TGF-b/Smad signaling system. EMBO J. 2000; 19:1745-54.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.











 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.